Kaspa: The Next Bitcoin?
By Andy Wang | Crescent City Capital Market Analyst Intern
What Is Kaspa?
Drawing inspiration from Satoshi Nakamoto‘s work, the project strives to preserve fundamental aspects of the Bitcoin (BTC) consensus. These include the PoW mining method, a deflationary economic model, and decentralized decision-making processes.
Kaspa’s main mission is to address the persistent challenges affecting the scalability and speed of decentralized transactions. Traditional blockchains usually grapple with network congestion as they expand. Such challenges inevitably result in slower transaction times and increased fees.
Kaspa aims to overcome existing blockchain technology limitations by fundamentally changing how blockchains function. Kaspa has developed a distinctive protocol known as GhostDAG to achieve this goal. Underneath the protocol is a novel algorithm that enables the network to process transactions in parallel rather than sequentially. This approach significantly enhances the blockchain’s capacity and transaction throughput. As a result, it can facilitate instant transactions at a fraction of the cost they would otherwise incur.
Moreover, Kaspa is an open-source project, which means that it is built upon the efforts of a global community of developers. This expansive community maintains, improves, and innovates upon Kaspa’s foundational technology.
Kaspa Founders and Development Team
Kaspa was initially designed by research and development company DAGLabs, with investment support from PolyChain. However, Kaspa has evolved into a community project with no central governance or business model.
The founder of Kaspa is Yonatan Sompolinsky, a Postdoc CS at Harvard University and a member of the MEV Research Team. Yonatan’s contribution to the field of blockchain is notable, as his 2013 paper on the Ghost protocol is cited in the Ethereum Whitepaper.
Other key members of Kaspa’s development team include Shai Wyborski, a Cryptography Doctoral student; Michael Sutton, a CS Master; Mike Zak, a CS Undergrad; Elichai Turkel, a Cryptography researcher; and Ori Newman, a Developer.
Why is Kaspa Called the Next Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin works on the most secure PoW, it struggles with scalability. Other blockchains, including Ethereum, started using the less energy-intensive Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, its security is questionable. However, the Kaspa blockchain achieved scalability while working based on the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism.
The Kaspa blockchain is often referred to as the advanced Bitcoin blockchain, highlighting the similarities between the two. Major similarities include Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, halving events, and limited token supply. By addressing the scalability issue of Bitcoin, Kaspa took a step further and is emerging as the advanced and scalable blockchain in the industry.
How Does Kaspa Work?
The Highway Analogy is ideal for explaining what Kaspa sets out to achieve and how it accomplishes its objectives.
Think of a highway for data (such as transactions). In the case of traditional blockchains like Bitcoin, that highway has only one toll booth. During rush hours, the road is flooded with vehicles, forcing transactions (cars) to queue up one by one at the toll booth (miner) before proceeding. This bottleneck creates congestion, slowing travel (transaction processing) and driving up tolls (transaction fees).
To counter this problem, Kaspa uses a unique approach that combines the speed and scalability of directed acyclic graph (DAG) structures. At its core, Kaspa utilizes two primary protocols: PHANTOM and GHOSTDAG. These protocols aim to tackle the scalability trilemma by offering a solution that doesn’t compromise security or decentralization.
PHANTOM is a proof-of-work(PoW) protocol that adopts a DAG structure. Unlike a blockchain that operates on a single chain of blocks, a DAG allows for blocks to be added in parallel. This structure significantly increases the network’s throughput as multiple transactions can be processed simultaneously rather than sequentially.
Meanwhile, GHOSTDAG takes the DAG concept further by introducing a method to order these parallel blocks in a way that maintains the network’s security and consensus. It advances beyond the Nakamoto consensus by dynamically calling transactions in a DAG structure. This way, there is ample room to preserve security and consensus even with parallel block additions.
In other words, even though transactions are processed in parallel, the network can still agree on which transactions happened first.
Essentially, PHANTOM changes the game by introducing a DAG structure. This opens up multiple toll booths on the highway, allowing various cars (transactions) to simultaneously pass through in a parallel setting. Significantly reducing traffic congestion enables multiple transactions to proceed in parallel by opening up several toll booths on the highway.
However, unlike the toll booth, where the exact time of entry or exit might not be crucial, these timestamps are essential for transactions in blockchain networks. The correct sequencing is important to prevent issues like double-spending.
So now, with multiple toll booths operating in parallel, the challenge is to ensure that every car’s movement through the toll network is recorded in an orderly manner. This is where GHOSTDAG steps in.
It acts as an intelligent traffic controller system that dynamically manages the flow of cars (transactions) across all toll booths (miner confirmations). GHOSTDAG ensures that the order of transactions makes sense and maintains the integrity of the entire highway network (blockchain). Even with multiple booths operating simultaneously, GHOSTDAG keeps track of every car’s entry and exit sequence (transaction details).
What Makes Kaspa Unique?
- Unlike traditional blockchains with a single chain, Kaspa utilizes a BlockDAG (Directed Acyclic Graph). This allows for parallel processing of transactions, significantly increasing scalability and transaction speed.
- Kaspa also implements the GHOSTDAG protocol. This protocol acts as a traffic controller within the BlockDAG, ensuring smooth and secure operation by verifying transactions and maintaining the correct order.
- Unlike other blockchains where only one block is accepted per round, Kaspa utilizes all valid blocks, maximizing efficiency and minimizing wasted processing power.
- Increased processing capacity and competition for limited block space can lead to significantly lower transaction fees than traditional blockchains.
- Kaspa is specifically designed to handle a high volume of transactions. That makes it an ideal choice for widespread adoption.
Kaspa Tokenomics
The blockDAG architecture of Kaspa, combined with its rapid block rates, is intended to make KAS mining decentralized and offer effective solo mining even at lower hash rates.
Kaspa was fair-launched in November 2021, with no pre-mine, pre-sales, or coin allocations. The maximum supply of Kaspa tokens is set at 28.7 billion coins, and the emission schedule follows a halving pattern once per year, with smooth monthly reductions.
Market Recap
The live Kaspa price on March 23, 2024 is $0.140780 USD with a 24-hour trading volume of $63,037,140 USD. Kaspa is down 4.37% in the last 24 hours. The current CoinMarketCap ranking is #40, with a live market cap of $3,252,902,983 USD. It has a circulating supply of 23,106,296,913 KAS coins and a max. supply of 28,700,000,000 KAS coins.
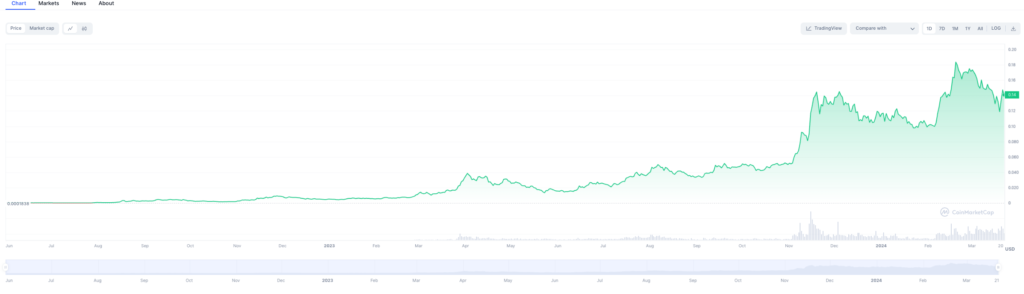
Analysis:
From the above historical movement of Kasper, we can clearly see the positive momentum of this token. With that being said, the token is up by a staggering 74,000% since its launch in July 2022, according to data from CoinMarketCap. The daily chart highlighted a significant resistance level at $0.189849 (screenshot shown below), which is also Kaspa’s ATH on 20 February 2024. On the flip side, I identified a low support level at $0.092937.
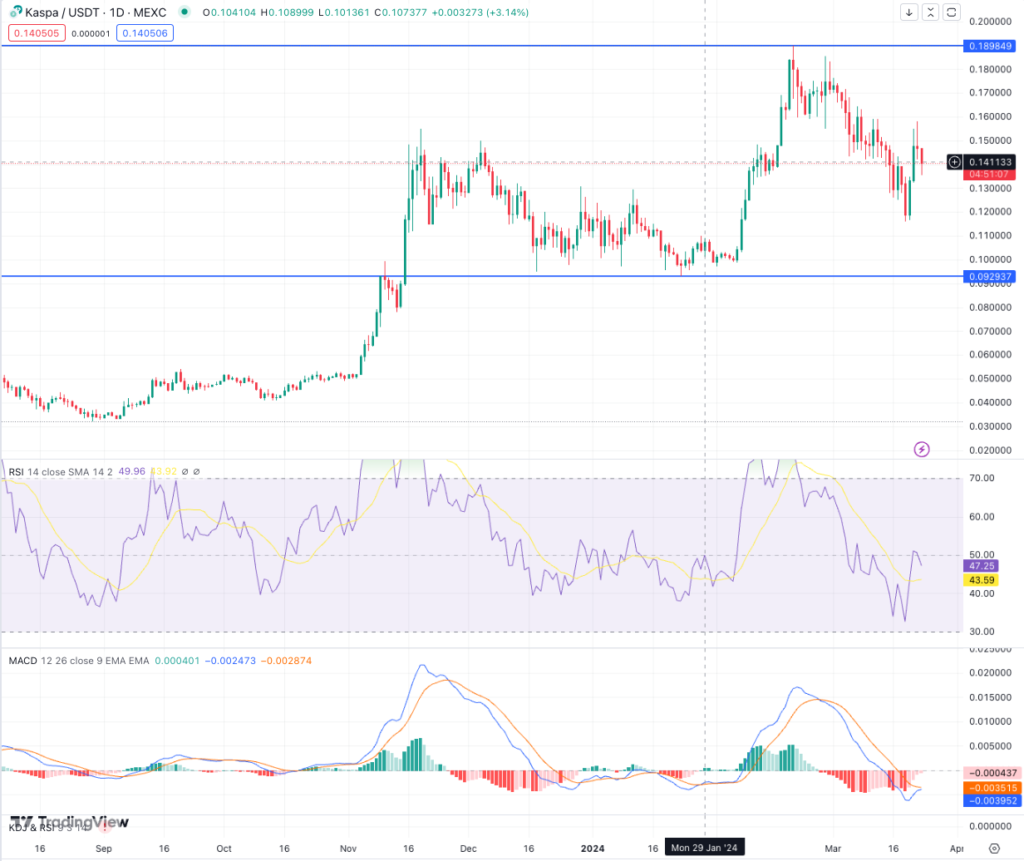
My piece of Kaspa’s price prediction in 2024 hinges on its daily chart. For the majority of the observed period, the market exhibited bearish control. However, the bulls were not entirely absent.
The analysis period began with KAS maintaining its lowest support level at $0.09. The latter part of January saw a determined attempt by the bulls to push the price above the $0.10 resistance. This effort was short-lived, as it met with rejection at the close of January.
This initial failure did not deter market optimism. The bulls initiated a more vigorous rally close to the end of the first week of February. The uptrend that ensued was notable, with the price ascending to meet resistance at $0.14.
Bullish resilience became evident as the buyers exerted substantial pressure to flip this resistance into a support level by mid-February. This momentum was carried forward, propelling KAS to its peak resistance at $0.18. On February 20, KAS reached a new all-time high (ATH) of $0.189, encapsulating a brief but significant period of bullish dominance.
Nonetheless, this peak was followed by a reversal in fortune. The subsequent decline saw temporary respite at the $0.16 support. The bulls made another futile attempt to rally towards the end of February.
This was met with increased bearish pressure. As March progressed, the asset dipped below the $0.16 support. It eventually stabilized at the current support level of $0.14.
The trading price reflected the renewed bearish sentiment and the ongoing tussle for dominance at the $0.14 support. Should the bears succeed in breaching the $0.14 support, the market may seek support at the next potential halt at $0.13. In the context of an exacerbated bearish outlook, KAS’ valuation might retreat to a lower boundary of $0.10.
Conversely, if the bulls regain their footing and reclaim the $0.16 support, there’s potential for a resurgence to $0.18. Sustained rallies can lead the price to overcome the current established peak resistance, paving for the price to elevate toward the $1 benchmark within the annual timeframe. This bullish outlook is underpinned by a significant appreciation of approximately 3443% over the preceding year.
Now, with enough technical discussions, I want to raise a question → Is Kaspa better than Bitcoin? The answer from my point of view is –
Yes, Kaspa blockchain is better than Bitcoin because of its operating mechanisms. The BlockDAG architecture allows Kaspa to validate parallel blocks and enhances its scalability. This is the major advantage of Kaspa compared to Bitcoin.
Kaspa is a promising blockchain initiative, blending the robust security of PoW with rapid block processing and minimal confirmation durations. Thanks to its distinctive characteristics and dedication to scaling, I sincerely believe Kaspa is poised to emerge as a significant force in the world of decentralized apps.
The Kaspa blockchain is the first-of-its-kind blockchain that combines both PoW consensus mechanisms with scalability. Its GHOSTDAG protocol allows the network to process parallel blocks at the same time. Overall, Kaspa blockchain stands at the forefront of innovation when it comes to offering security, scalability, and an efficient blockchain for developing dApps.
At the same time, KAS, Kaspa’s native cryptocurrency, boasts strong tokenomics and a respectable history. It holds promise, yet investing in it requires a clear understanding of the risks inherent in cryptocurrency investments.
Given the significant impact of market volatility and price fluctuations, it is important to closely monitor the token price movement on a daily basis. With the Bitcoin Halving is approaching, and as historical presented, everytime BTC Halving happens, the BTC price along with the market sentiment will go down during the halving period, once the halving is over, the BTC price will sky-rocket, as does the broad crypto market. Therefore, in terms of the next 12 to 18 month period, I would recommend locking in with this BTC v2 token as it demonstrates numerous potential price surges. However, at the same time, investors should take great care of their positions.
Reference:
https://twitter.com/KaspaCurrency?ref_src=twsrc%5Egoogle%7Ctwcamp%5Eserp%7Ctwgr%5Eauthor
https://kaspa.org/about-kaspa/
https://uphold.com/blog/crypto-basics/what-is-kaspa-how-does-it-work

